The Cosmos ecosystem represents a decentralized network comprised of independent blockchains. Known as ‘Zones’ within the Cosmos framework, these blockchains run parallel to each other, ensuring seamless interoperability and impressive scalability. This interconnectedness has led the Cosmos community to affectionately dub it the ‘Internet of Blockchains,’ a testament to its remarkable potential.
Cosmos prides itself on its customizability and open-source nature. These attributes greatly simplify the process for both users and developers, allowing them to facilitate transactions and protocols between various Cosmos Zones effortlessly. It’s worth noting that all Zones in this expansive ecosystem are fully compatible and intricately linked to the heart of it all – the Cosmos Hub.
At the core of the Cosmos network lies the Cosmos Hub, a proof-of-stake (POS) blockchain that oversees the management of transaction records and statuses across all Cosmos Zones. So, let’s delve into the uniqueness of ATOM, the native token of the Cosmos Hub. ATOM plays a vital role in processing transactions and upholding network security.
Remarkably, millions of blockchain enthusiasts engage with Cosmos blockchains daily, often without realizing it. Notable chains that have thrived within the Cosmos Ecosystem include Binance Smart Chain, Cronos Chain, and Terra Chain.
What is Cosmos? Quick facts
- Cosmos is a collection of parallel blockchains, known as Zones, that operate cohesively and can interconnect seamlessly.
- Within the Cosmos network, users enjoy effortless token migration between distinct Cosmos Zones.
- At the core of the Cosmos network stands the Cosmos Hub, a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain that serves as the central hub for the entire ecosystem.
- ATOM, the native token of the Cosmos Hub, holds a pivotal role in staking, governance decisions, and covering gas fees within the network.
- Remarkably, Cosmos serves as the foundation for numerous popular chains like Binance Smart Chain and Cronos, highlighting its extensive influence in the blockchain industry.
How does Cosmos work?
Cosmos has a clear mission to simplify the development process while enhancing connectivity across its ecosystem of networks. The structure of Cosmos Zones is designed with three fundamental layers in mind:
- Application Layer: This crucial layer takes charge of managing on-chain transactions and ensuring the network’s state is maintained efficiently.
- Consensus Layer: The consensus layer is responsible for establishing consensus and overseeing the creation of new blocks within the network.
- Networking Layer: The networking layer is responsible for facilitating seamless communication between various Cosmos Hub Zones, ensuring a robust and interconnected ecosystem.
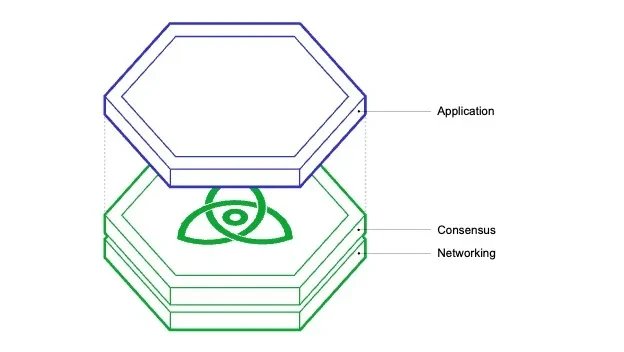
Expanding on the core elements of these three tiers, the Cosmos Ecosystem harnesses the capabilities of a robust collection of Open Source functionalities. These resources empower developers to craft applications that prioritize security, personalization, and scalability, all while ensuring seamless compatibility within Cosmos Zones. This adaptability represents a distinctive attribute that resonates strongly with the developer community’s preferences when it comes to Cosmos. So, what steps has Cosmos taken to simplify the development process, and what is the underlying mechanism driving the Cosmos ecosystem’s functionality?
Cosmos Software Development Kit
The Cosmos Software Development Kit, commonly referred to as the Cosmos SDK, plays a pivotal role as an indispensable resource within the Cosmos Ecosystem. It streamlines the process of crafting and launching fresh Cosmos Zones, eliminating the need for developers to commence their work entirely from square one. One can liken the Cosmos SDK to a ready-made blockchain blueprint, offering a more accessible route for envisioning and creating new Cosmos Zones.
Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC)
The Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC) stands as a pivotal component in the Cosmos network, complementing the Tendermint BFT engine’s capacity for vertical scaling and straightforward deployment of Cosmos zones. IBC emerges as a vital instrument, enabling seamless interaction and data transfer between various chains within the network. Its versatility lies in its ability to facilitate token and data exchanges across interconnected chains, irrespective of their individual architectural designs. This means that even chains with varied consensus mechanisms and applications can effectively exchange information, thanks to IBC.
Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerance
The Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) system is renowned for its efficient Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Characterized by its impressive performance, it boasts a rapid blocktime of merely one second. Furthermore, it can handle approximately 10,000 transactions every second, coupled with the advantage of instant finality. This robust framework ensures both speed and reliability in transaction processing.
What is ATOM and where is it used?
ATOM is the fundamental cryptocurrency within the Cosmos Ecosystem. Its primary use is to cover gas fees and facilitate transaction processing within the Cosmos Hub. Beyond these basic functions, ATOM plays a significant role in network security and governance. Holders of ATOM can stake their tokens to run a validator node in the Cosmos Hub, contributing to the network’s security while earning staking rewards.
Additionally, ATOM is integral to the governance process of the Cosmos ecosystem. It allows token holders to engage in and influence decisions about the ecosystem’s future developments. In this governance structure, the influence in voting on various proposals is generally proportional to the amount of ATOM one holds, giving larger stakeholders a more significant say in the direction of Cosmos.
Cosmos history
The concept of the Cosmos Ecosystem dates back to 2014, when its founders, Jae Kwon and Ethan Buchman, envisioned the potential of integrating their Tendermint consensus model with blockchain technology. This integration aimed to create a network of interoperable blockchains.
Backed by the Swiss-based Interchain Foundation, Tendermint Inc made significant progress in the development of this innovative project. By 2016, this project had been christened Cosmos. The following year, in 2017, Cosmos marked a milestone with its ATOM Initial Coin Offering (ICO), which was a resounding success, selling out in just 29 minutes. The funds raised from this ICO were instrumental in furthering the development of key components like the Cosmos SDK and the Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol (IBC).
On March 13, 2019, the Cosmos Mainnet was officially launched, signaling a new era in the cryptocurrency realm. Since its inception, the Cosmos ecosystem has garnered considerable attention and adoption in the cryptocurrency market. Prominent blockchains, including Binance Smartchain and THORChain, have been launched on the Cosmos network, underscoring its growing influence and importance.
ATOM tokenomics
ATOM, the core cryptocurrency of the Cosmos Hub, boasts a circulating supply of about 285 million tokens. Unlike many other cryptocurrencies, ATOM doesn’t have a capped maximum supply.
Back in 2017, the Cosmos team successfully completed three funding rounds, collectively garnering $17 million. Messari reports that the initial allocation of 236,198,958 ATOM tokens was divided in the following manner:
- Tendermint Inc and the Interchain Foundation each received 10% of the total.
- Strategic participants and early adopters were allocated 7.1%.
- Contributors to the seed round were given 5%.
- The public ICO saw the largest share, with 67.9% of tokens distributed to contributors.
A notable aspect of Cosmos’s approach was the decision not to earmark any ATOM tokens for market liquidity or community incentives. Currently, the original vesting period is complete, meaning all the initially distributed tokens are fully unlocked and in circulation.
How is ATOM created?
The process of ATOM generation is intricately linked to the Cosmos Hub’s Proof of Stake (PoS) system. In this ecosystem, ATOM tokens are continuously generated and allocated as staking rewards. These rewards are given to validator nodes, whose role is pivotal in maintaining network security and managing transaction processing on the chain. A unique aspect of ATOM is its inflationary nature; there is no capped limit to its supply, and new tokens are regularly introduced into the system.
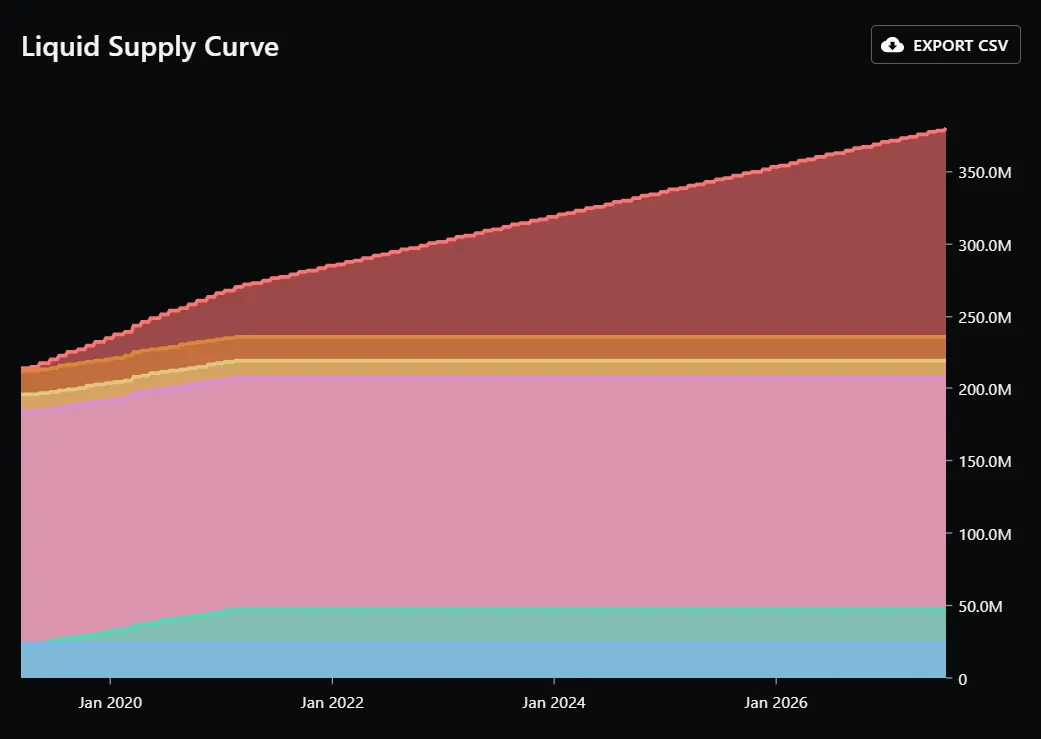
When it comes to the inflation rate of Cosmos, it’s not a static figure. The inflation rate of ATOM tokens is dynamic, varying in response to the proportion of tokens staked within the network. Essentially, the more ATOM tokens are staked, the lower the inflation rate becomes. This variable rate of inflation, which is recalculated with every new block, makes it challenging to set a consistent inflation rate for ATOM. Typically, the inflation rate for ATOM oscillates between 7% and 20%, with variations depending on the staking activity within the network.
What is Cosmos’ competition and how do they stack up?
Analyzing Cosmos’ position in the blockchain arena involves examining its unique structure and comparing it with other platforms, such as Polygon, that also aspire to be the ‘internet of blockchains.’ The Cosmos Hub, while central to the Cosmos protocol, is not the biggest blockchain within its ecosystem. This contrasts with other blockchain networks where the central chain typically holds the most significant value.
To assess the competitive landscape, key metrics like total value locked (TVL) and market capitalization are crucial. For instance, as of December 2023, Polygon demonstrated a higher market cap (around $5.6 billion) and TVL (approximately $1.6 billion) compared to the Cosmos Hub, which had a market cap of $2.5 billion and a TVL of $310,000. However, this comparison shifts when considering the entire Cosmos ecosystem, including its interoperable blockchains. Collectively, these blockchains in the Cosmos network boast a market cap exceeding $50 billion, dwarfing Polygon’s figures and positioning Cosmos as a formidable contender in the global cryptocurrency market, second only to Ethereum as a platform.
It’s important to note that these statistics were impacted by the fall of Terra Luna, once a top-tier cryptocurrency and a key component of the Cosmos network. Before its dramatic collapse in May 2022, Terra Luna significantly contributed to the overall value of the Cosmos ecosystem. Despite this setback, Cosmos still maintains a strong position in the blockchain landscape.
Cosmos partnerships and investors
The Cosmos network has garnered robust institutional backing from prominent companies worldwide. Renowned investment firms such as 1Confirmation, Blocktree Capital, Outlier Ventures, and Dragonfly Capital have shown their trust in Cosmos. These seasoned financial backers have played a pivotal role in guiding the Cosmos Team’s expertise and fostering their advancement in the cryptocurrency realm.
One of the most significant milestones achieved by the Cosmos Ecosystem is its collaboration with the Binance Smart Chain. The Binance Smart Chain stands as the second-largest blockchain in terms of Total Value Locked (TVL) within the industry. In their quest to develop their blockchain, the Binance Smart Chain team was deeply impressed by the architectural framework offered by Cosmos. Consequently, they deemed it the natural choice for the foundation of their network
Cosmos strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
Cosmos Strengths
The Cosmos Hub boasts several notable strengths, including its ability to maintain low gas fees, ensure instant transaction finality, and support an impressive transaction throughput of approximately 10,000 transactions per second. Beyond this, the infrastructure offered by Tendermint BFT and Cosmos SDK facilitates the straightforward launch of new chains within the Cosmos Ecosystem, making it an attractive option for emerging projects.
Cosmos Weaknesses
While Cosmos offers staking rewards, they can be subject to fluctuating rates, and there exists a risk of emitting ATOM tokens at a high inflation rate, reaching as high as 20%, over extended periods. Additionally, Cosmos lacks deflationary burn mechanisms akin to Ethereum and Polygon’s EIP 1559, which could help counteract this inflationary pressure.
Cosmos Opportunities
The Cosmos Ecosystem and its architectural design present significant growth and partnership opportunities. As an increasing number of enterprises seek entry into the Web3 industry, Cosmos is well-positioned to facilitate their onboarding. Leveraging the Cosmos Ecosystem, new companies can seamlessly launch their own blockchains and rapidly expand their operations with blockchain technology. This versatility is highly appealing to many businesses looking to leverage the benefits of Cosmos.
Cosmos Threats
One of the prevailing threats to Cosmos is the limited availability of many blockchains and native tokens built on the platform on popular cryptocurrency exchanges. Currently, acquiring some of these tokens requires purchasing ATOM and bridging them through the Cosmos Hub. As these projects and tokens gain prominence, they are likely to find their way onto mainstream exchanges, potentially reducing the reliance on ATOM. In this context, there is a concern that Cosmos might face challenges stemming from its own success.
However, this issue could be mitigated by the continuous influx of new projects opting to build on Cosmos, drawn by the successes of previous endeavors. These fresh chains may eventually supplant older projects that initially launched on Cosmos, thus rejuvenating the utility and relevance of the ATOM token within the ecosystem.
Cosmos roadmap
The remarkable expansion of the Cosmos Ecosystem has ignited curiosity about its future directions. The forthcoming milestone on the Cosmos roadmap is the introduction of the v8-Rho upgrade.
This update promises to usher in a host of fresh enhancements across the Cosmos Hub, Cosmos SDK, and the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, including:
- Enhanced High-Level Multi-Signature Permissionless Accounts
- Introduction of Meta Transactions
- Refinements to the Governance Module
- Incentivization for IBC Relayers
This update demonstrates Cosmos’ commitment to continual improvement and innovation within its ecosystem.
Cosmos updates, news, highlights
Cosmos has emerged as a prominent player in the cryptocurrency industry, primarily because of its capacity to empower applications to swiftly create and manage their own blockchains. In response to the escalating gas fees and scalability challenges experienced on Ethereum, many projects are actively exploring the possibility of migrating their platforms and services to more accessible networks, with Cosmos being a prime contender.
Cosmos founder Jae Kwon has put forth a proposal for a fork of the Cosmos network following a contentious governance vote (Proposal 848). This proposal sought to cap ATOM’s inflation at 10%, aiming to reduce the existing inflation rate of approximately 14% and lower staking rewards. While the proposal narrowly passed, it met with strong disagreement from Kwon.
Considering this discord, Kwon is contemplating the development of a fork named AtomOne, with the aim of providing an alternative governance system and addressing the internal divisions within the Cosmos community.
The Cosmos ecosystem has witnessed significant progress as well. Projects such as Umee and Osmosis, both built on the Cosmos platform, have joined forces to create a ‘DeFi Hub,’ which has the potential to bolster the DeFi sector within the Cosmos ecosystem. Additionally, the renowned decentralized finance platform, dYdX exchange, has made its source code public for an upcoming Cosmos-based network, signaling a growing acceptance of Cosmos technology among DeFi projects.
The Interchain Foundation (ICF), a key contributor to the Cosmos development, has announced plans to allocate $26.4 million in support of the ecosystem in 2024. This represents a slight reduction from the $40 million allocated in 2023. The funds will be primarily directed towards ensuring the optimal functionality of the Interchain Stack. Within this budget, $3 million will be dedicated to CometBFT, Cosmos’ Byzantine fault-tolerant engine; $4.5 million to the Cosmos SDK, and $7.5 million to the inter-blockchain communications protocol (IBC). This allocation underscores the continued commitment to advancing the Cosmos ecosystem.
Cosmos vs Polkadot: the interoperability race
Cosmos and Polkadot stand as prominent cryptocurrency projects with a primary focus on enhancing interoperability and fostering communication among various blockchain networks. While Polkadot enjoys greater recognition in the crypto space, recent developments such as the dYdX migration have sparked increased interest in Cosmos. In this comparative exploration, we’ll delve into the origins and key distinctions between these two innovative ventures.
Cosmos emerged onto the scene in 2014, spearheaded by the visionary Jae Kwon. Kwon’s impressive academic background boasts a Bachelor’s degree in computer science from Cornell University, renowned for hosting one of the world’s foremost computer science programs. In contrast, Polkadot finds its genesis with Gavin Wood, a notable Ethereum Co-founder responsible for co-inventing the Solidity programming language. Wood holds a PhD in human-computer interfacing from the University of York, further cementing his expertise in the blockchain realm.
Turning our attention to the underlying consensus mechanisms, Polkadot relies on a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus model complemented by its proprietary proof-of-authority mechanism. This unique combination empowers Polkadot’s primary chain, known as the relay chain, to handle a respectable throughput of up to 1,000 transactions per second. Additionally, it can currently extend its support to accommodate up to 100 parachains.
In contrast, the Cosmos Hub operates on the Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) PoS model, boasting an impressive transaction processing capability of up to 10,000 transactions per second. The Cosmos network boasts a remarkable 49 Cosmos Zones, with no predefined limit in sight. This expansive ecosystem grants Cosmos the versatility and potential to scale beyond the confines of Polkadot’s capabilities.
One pivotal distinction to note is the interdependency of Polkadot parachains on the central Polkadot relay chain and its underlying architecture. Should a flaw or bug surface within the core Polkadot system, it could potentially impact the performance of its parachains. Conversely, Cosmos Zones operate autonomously, functioning independently of one another. In practice, this means that if one Zone within the Cosmos network experiences issues or congestion, it will not adversely affect the operational efficiency of alternative zones, safeguarding the overall network performance.
In conclusion, Cosmos and Polkadot, while sharing a common goal of enhancing blockchain interoperability, diverge in their origins, consensus models, and network architectures. Each project brings its unique strengths and considerations to the table, offering distinct advantages for those seeking to navigate the dynamic world of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
The final word
Often referred to as the ‘internet of blockchains,’ Cosmos represents a revolutionary network comprising independent, interoperable blockchains known as ‘Zones.’ At the heart of this ecosystem lies the Cosmos Hub, which employs its native token, ATOM, to facilitate governance and transactions.
Cosmos offers a decentralized framework that empowers both users and developers to easily tailor and incorporate protocols, enabling seamless interactions across various Zones. What sets Cosmos apart is its open-source architecture and layered structure (Application, Consensus, Networking), complemented by tools like the Cosmos SDK and IBC, which enable effortless scalability and the creation of fresh Zones. The foundation of all these functionalities rests on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain.
Prominent chains such as Binance Smart Chain and Cronos, both integral parts of the Cosmos network, exemplify its extensive adoption and the promising prospects it holds for future expansion.


